On a winter morning, you reluctantly walked into the bathroom after being suffocated by urination, everything was ready, but found that you wanted to pee but couldn’t…
I believe that most people have had the experience of holding back urine: the urge to urinate is raging, the bladder is full and painful, and it feels that the urine can break through the resistance of the “fence” at any time and rush out.
But there are also people who want to pee but can’t:
Obviously I felt the urge to urinate, but only a drop or two came out when I went to the toilet.
My brain received the signal to urinate, and as a result, I went to the toilet for a long time and still couldn’t urinate.
Just because I couldn’t urinate, I ran to the toilet N times, and finally I held back a little pee.
After intermittently urinating, I still feel that the urine is not clean…
If this happens frequently, be careful that you may have urinary retention problems! The urine was “blocked” in the middle of the road, and couldn’t get out.

What is urinary retention?
Urine is composed of waste filtered by the kidneys from the blood. After filtering by the kidneys, the urine will flow to the bladder and then be excreted through the urethra. Urinary retention refers to the phenomenon of urine stagnation in the bladder that cannot be discharged on its own. Normally it’s divided into acute urinary retention and chronic urinary retention as follows:
Acute urinary retention:
Acute urinary retention is more common in men, with a male-to-female ratio of about 13:1, and increases with age. The bladder can suddenly be unable to discharge full urine, resulting in bladder distention pain, it requires immediate medical attention.
Chronic urinary retention:
The patient’s bladder function will gradually decline, resulting in excess urine retention in the bladder, so that the patient often feels that he wants to urinate but can’t urinate.
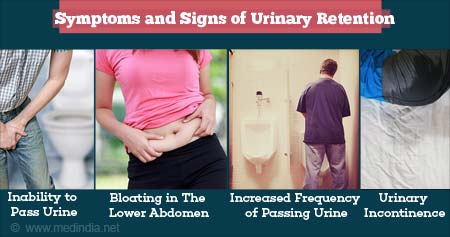
What are the symptoms of urinary retention?
Acute urinary retention:
- Your bladder is too full with urine and you cannot move around freely
- Severe pain, swelling in the lower abdomen
Chronic urinary retention:
Symptoms of chronic urinary retention are often difficult to detect. Here are five common symptoms:
- Difficulty urinating
- Inability to completely empty the bladder when urinating
- Frequent urination but decreased urine output
- Urinary incontinence
- mild lower abdominal pain
4 Ways to Diagnose Urine Retention
- Bladder Scan: Your doctor will use an ultrasound to check the amount of urine remaining in the bladder, as well as the presence of stones and lumps.
- Cystoscopy: If the diagnosis cannot be made through imaging examination, a cystoscope is used to insert a thin tube with a micro camera at one end into the urethra to directly check the state of the bladder. If problems are found after diagnosis, further examinations must be obtained.
- Urodynamic testing: During the examination, a urethral catheter and anal canal will be placed to test the pressure in the bladder, to understand the dynamic process of the patient’s urine storage and urination, and to judge the bladder emptying situation.
- Electromyography: Uses sensors to measure the activity of the bladder and urethral sphincter muscles and nearby muscles and nerves.
Top 5 Causes of Urine Retention
Urine retention can be caused by infection, stones or medication. The following are 5 common causes:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Prostatic hyperplasia increases the size of the prostate gland, which may compress the urethra or bladder neck, resulting in posterior urethral occlusion and inability to urinate, and may also cause symptoms such as slow urination, laborious urination, thin urine line, dribbling, and incomplete urination. Note 1
- Prostatitis
Prostatitis can cause local congestion and swelling, pressure on the urethra, and symptoms such as waiting for urine and straining to urinate.
- Urinary tract stones: Each year, approximately 0.1% of adults in the United States are hospitalized for urinary tract stones. Urinary tract stones refer to one or more hard “small stones” in a certain part of the urethra that prevent you from urinating smoothly. These stones can be classified as kidney stones, ureteral stones or bladder stones. It can also be accompanied by pain, bleeding, urinary tract obstruction, or infection when you pee tickly.
- Diabetes: About 20% to 60% of diabetic patients will develop bladder disease, mainly due to the high blood sugar in the body that causes nerve axonal lesions, which makes the detrusor activity worse, which in turn makes patients prone to unclean urine and urine retention. and overflow incontinence.
- Psychological factors
Some people feel nervous and panic when urinating, and this state leads them to be too nervous when urinating, which makes the bladder detrusor contract weakly, and the urethral sphincter is tight, so it is not easy to urinate.
The dangers of urinary retention
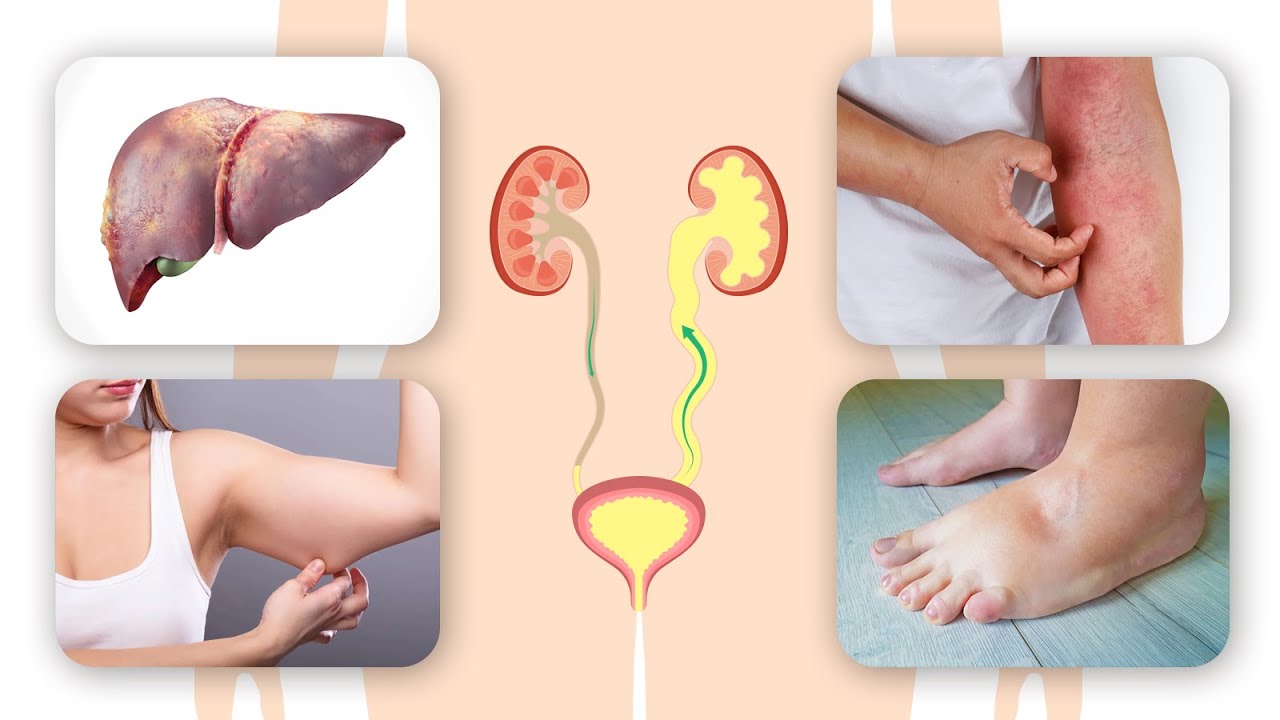
The residual urine will continuously stimulate the tension receptors in the bladder, stimulate the detrusor muscle contraction, and constantly feel the feeling of wanting to urinate, but due to insufficient contraction force, unable to urinate when going to the toilet, resulting in more fatigue of the detrusor muscle, The vicious circle continues. Once the residual urine volume has been more than 50cc, it is easy to breed bacteria, causing repeated urinary tract infections, and even damage to bladder and kidney functions, leading to uremia.The residual urine will result in a heavy bladder , prone to backache, back pain symptoms.
4 Common treatments for urinary retention
There are two main focuses in the treatment of urinary retention:
- Use medication to relax bladder neck muscles or prostate urethra pressure to increase urine flow.
- Use a urinary catheter to help the patient drain residual urine.
Listed below are 4 common treatments for urinary retention:
- Urinary tract smooth muscle action agent: A common drug is Bethanechol chloride, which can excite the parasympathetic nervous system, increase the tension of the bladder urinating muscle, and promote smooth urination.
- Alpha-adrenergic blocker: Alpha-adrenergic blocker is currently the most commonly used drug for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms caused by prostate hypertrophy. Improve the effect of urine retention.
- Antibiotics: If there is a problem of urinary retention due to infection after surgery, the doctor will first find the source of the infection, and then use antibiotics for the next stage of treatment for the patient.
- Urinary catheter: When acute urinary retention occurs, the physician will place a urinary catheter or catheterize the patient to relieve the patient’s discomfort, and the duration of the urinary catheter is related to the degree of urination at that time.
- Self-catheterization: For patients with chronic urinary retention, learning to self-catheterize can save the inconvenience of having to carry a urine bag for a long time, and can reduce the risk of urinary tract infection caused by long-term placement of a catheter. Note 1
A study of evaluating the management of acute urinary retention associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia ( 6074 men catheterized for painful AUR were enrolled) showed that In most cases, an α(1)-blocker is prescribed before TWOC and significantly increases the chance of success. Prolonged catheterization is associated with an increased morbidity. Note 2
How to prevent urinary retention?
For women – prevention of cystitis is key, which is mainly a bacterial infection and is prone to acute cystitis.
- Keep the perineum clean and avoid local bacterial retrograde infection, especially in women during menstruation, before and after intercourse, the body’s immune system is low, and cystitis may be induced.
- Menopausal women, because the level of estrogen decreases, can apply estrogen ointment locally, which can improve the vaginal environment, increase the number of lactobacilli, remove pathogenic bacteria, reduce the ability to reproduce, and can effectively reduce the incidence of cystitis.
- Kegel exercise: Kegel exercise is a pelvic floor muscle strengthening exercise. It can not only exercise pelvic floor muscles, but also improve bladder and bowel function. In addition to helping prevent urinary retention, it is also often used to improve urinary incontinence in postpartum women.
For men – prostatitis prevention is key:
- Drinking more water and urinating more, high concentration of urine will stimulate the prostate, and long-term adverse stimulation is harmful to the prostate. Drinking more water can not only dilute the blood, but also effectively dilute the concentration of the urine.
- Avoid holding back urine: If the urge to urinate strikes, you should go to the toilet as soon as possible, otherwise holding back urine will easily weaken the bladder, increase the chances of urinary tract infections and stones, and lead to urinary retention.
- Pay attention to abstinence in sexual life, avoid repeated congestion of the prostate, and give the prostate sufficient time to recover and repair.
For both men and women, here are a few things to keep in mind:
- For bladder training and expansion, patients need to drink water regularly during the day, 200ml per hour; and try to prolong the interval between urination, which can gradually increase the bladder capacity and help store urine.

- Appropriate exercise, sweat volatilization, detoxification, nourishing the kidney, promoting the body’s blood circulation can also promote the circulation of kidney blood, which is conducive to the formation and discharge of original urine.

- Strengthening pelvic floor muscle training can effectively exercise the flexibility and stretch of the bladder detrusor and sphincter muscles, and can effectively control urination.
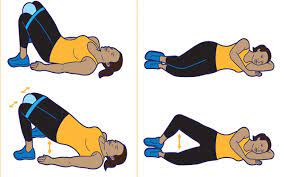
- More relaxation, regular work and rest, taboo sedentary is also a very important part of life conditioning.

- Adjust eating habits: You should avoid drinking cold drinks or stimulating diets (such as alcohol, spicy food, etc.), and drink less water before going to bed, which can reduce the stimulation of the bladder and reduce the risk of urinary retention.

In short, the feeling of incomplete urination is a common signal of urological diseases. Once the above symptoms appear, it is necessary to visit the urological outpatient clinic in time, improve relevant examinations, and clarify the cause is the key to treatment.